WEATHER FORECASTS
National Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology
NIMH issues weather forecasts based on numerical models, ground measurements, radar and satellite information
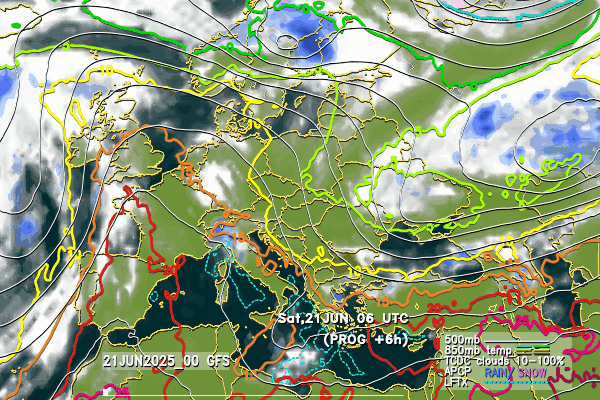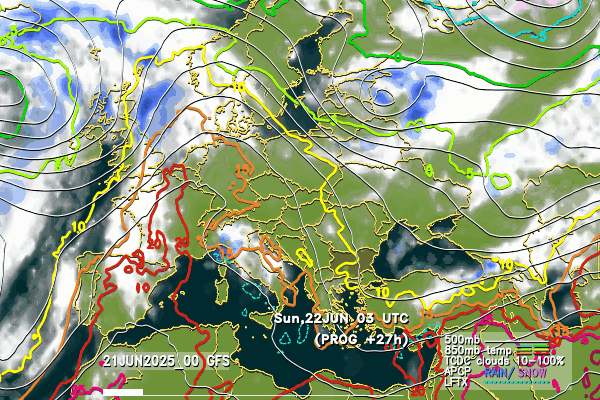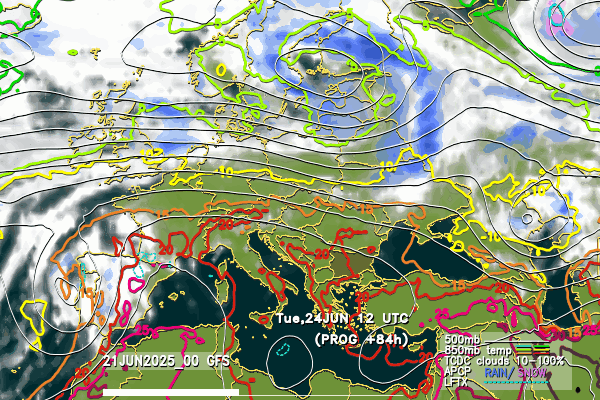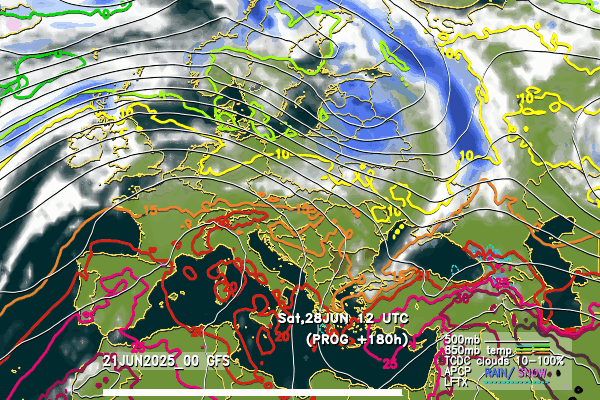
NIMH, together with the meteorological services of 25 other European and North African countries, is a member of the international consortium ACCORD (A Consortium for Convection-scale modeling Research and Development), where the regional numerical models ALADIN and AROME are developed. The configuration and maintenance of the hydrostatic ALADIN-BG and the non-hydrostatic AROME-BG at NIMH is carried out by the team of the "Numerical Modeling" section, "Forecasts and Information Services" department. The configurations of the operational numerical models are the following:
ALADIN – BG (hydrostatic)
- horizontal resolution of 5 km,
- 105 vertical levels,
- time step of 300 s.
- forecast range of 72 hours twice daily (at 06 and 18 UTC) and 48 hours twice daily (at 00 and 12 UTC); the domain of integration is centered in Bulgaria and covers almost the entire Balkan Peninsula.
AROME – BG (cloud-resolving)
- horizontal resolution of 2.5 km,
- 90 vertical levels,
- time step of 60 s.
- forecast range of 48 hours four times daily (00, 06, 12 and 18 UTC); the domain of integration covers Bulgaria and surroundings.
Below follow animated forecasts of temperature, wind, cloud cover and precipitation from the ALADIN-BG and AROME-BG models. For a detailed view you can visit this page
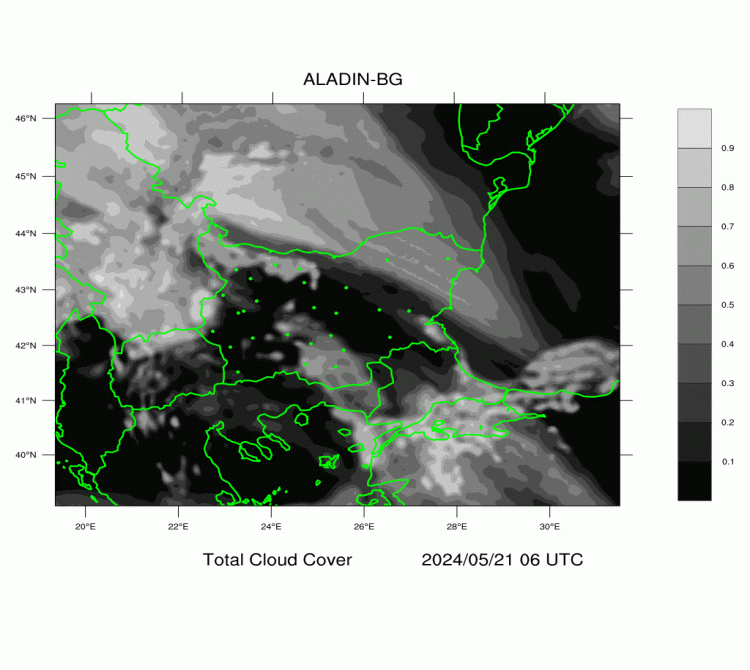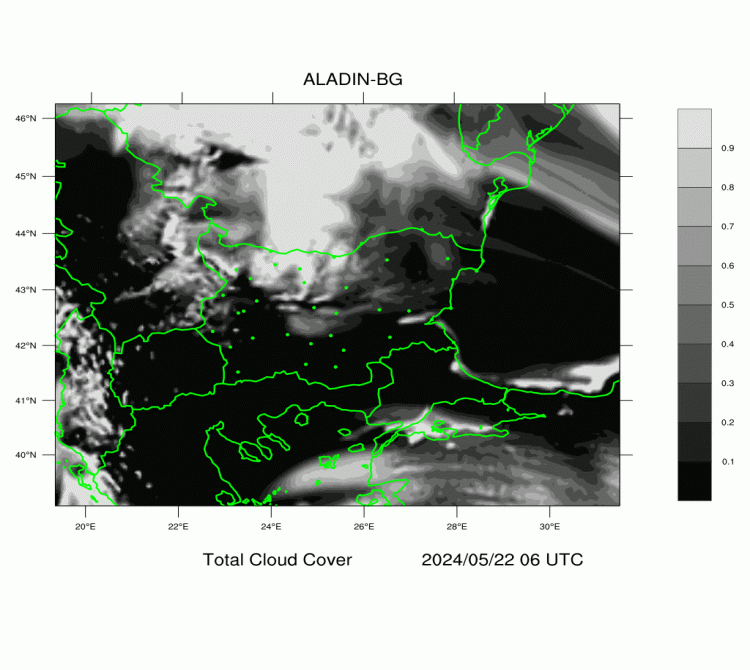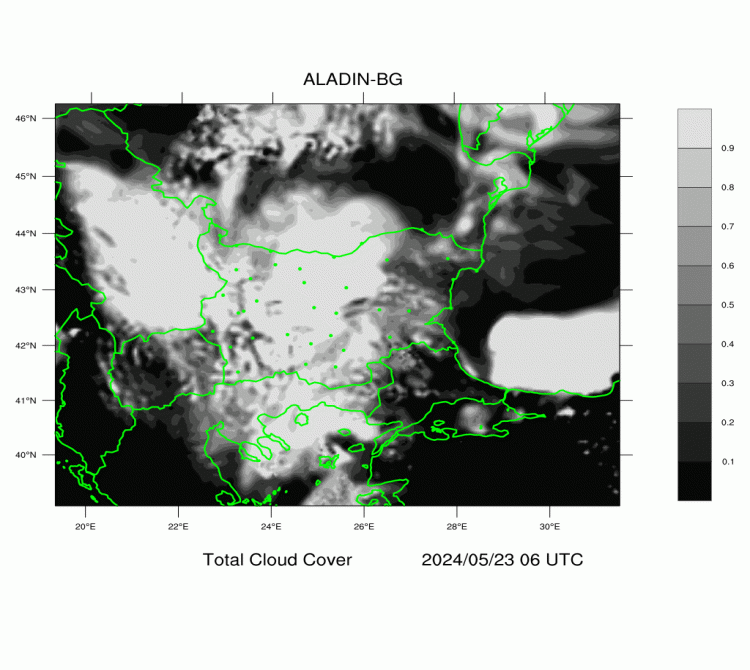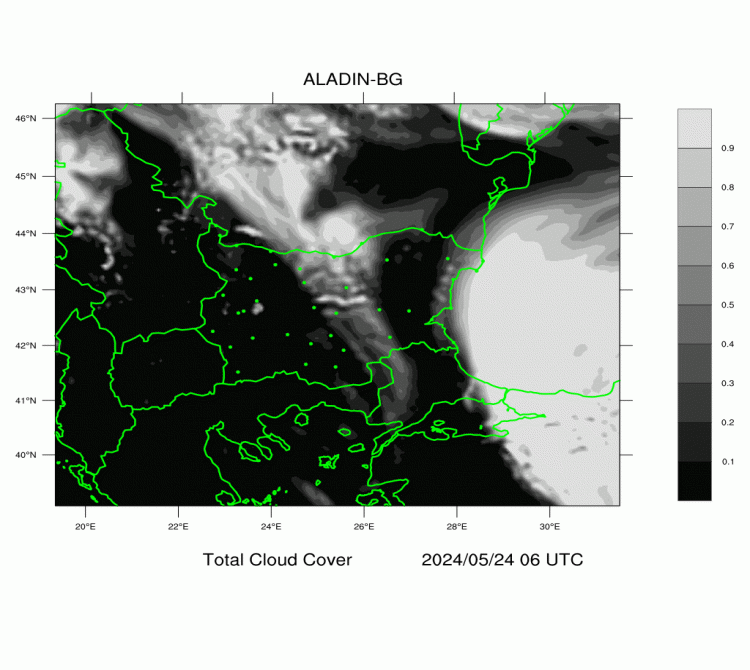
ALADIN-BG—Clouds
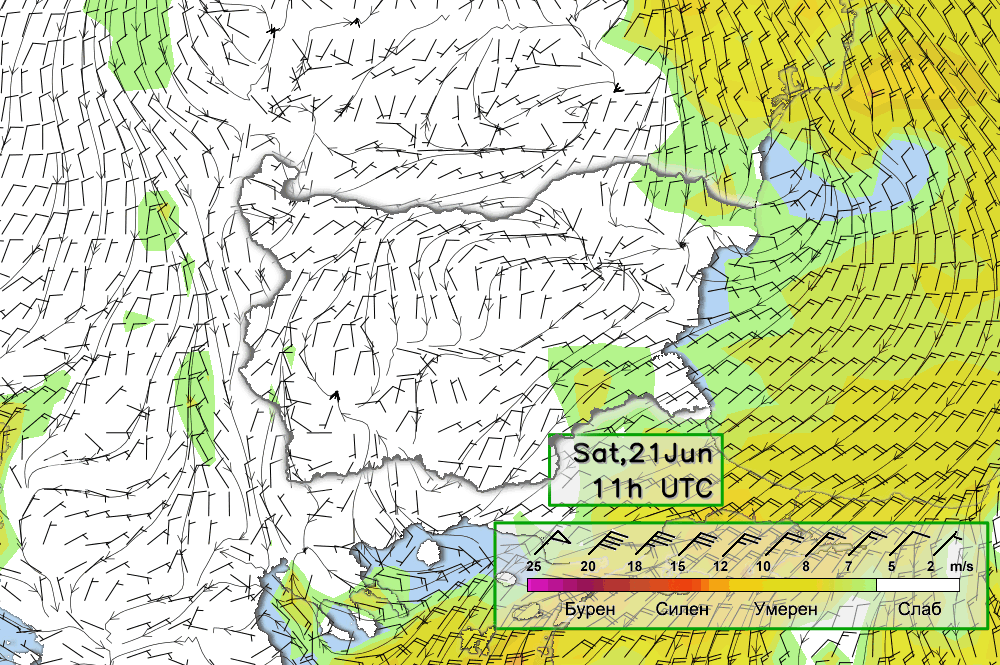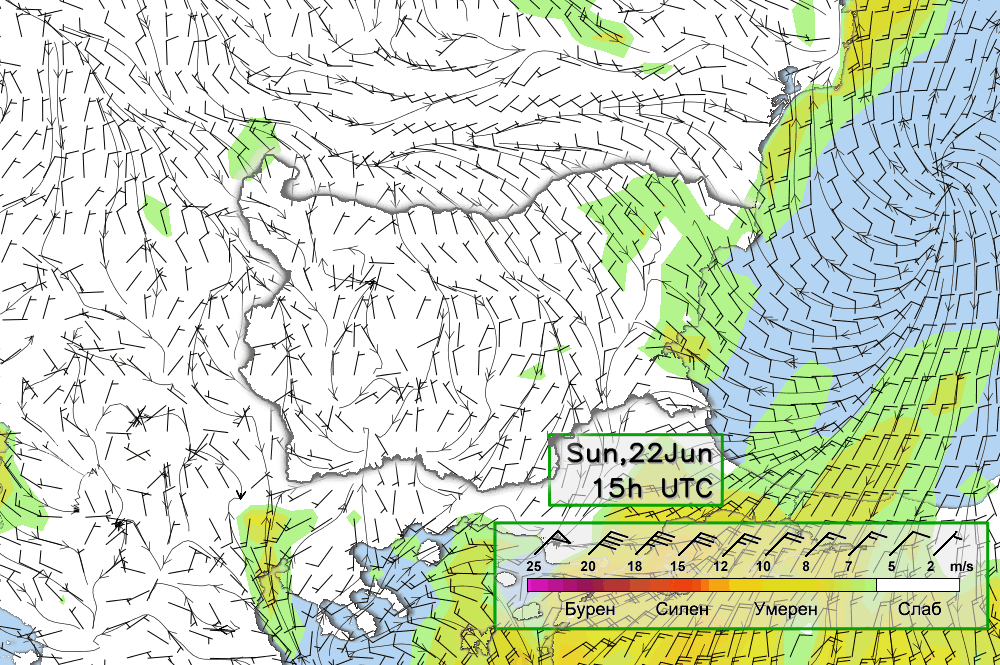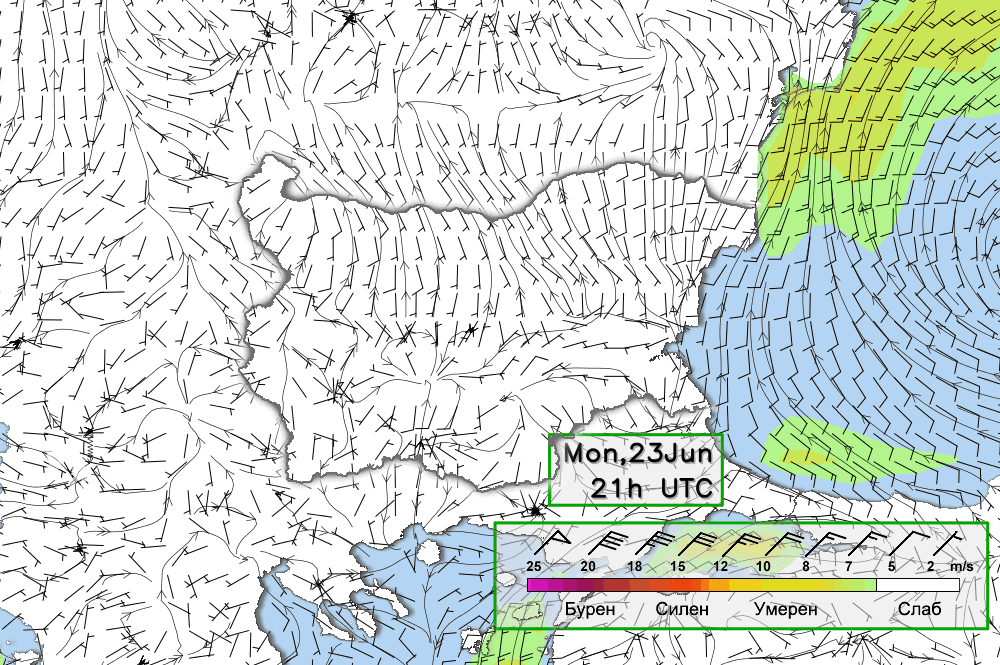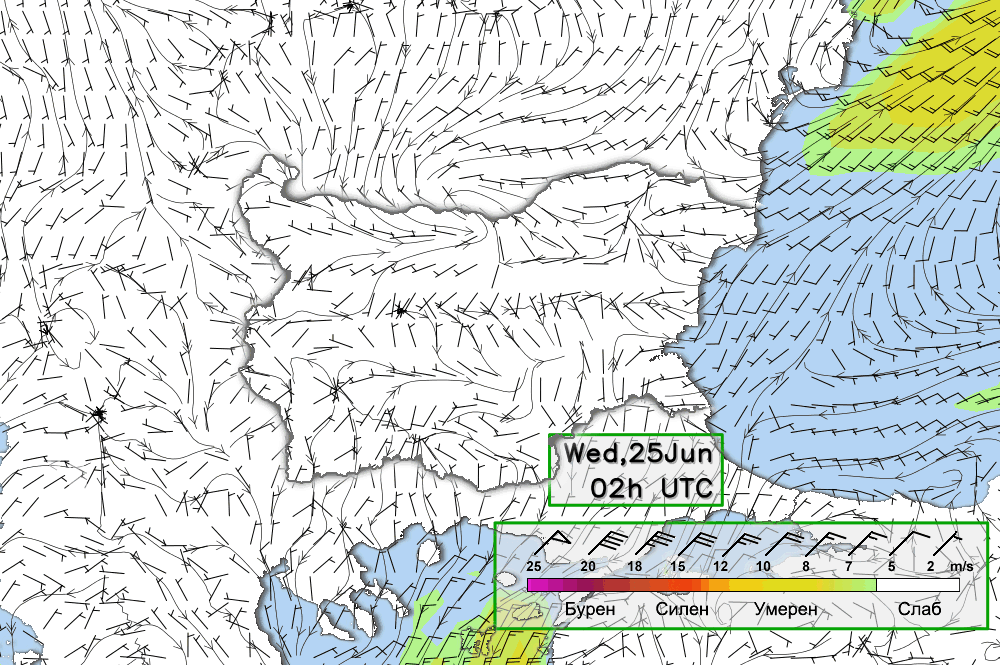
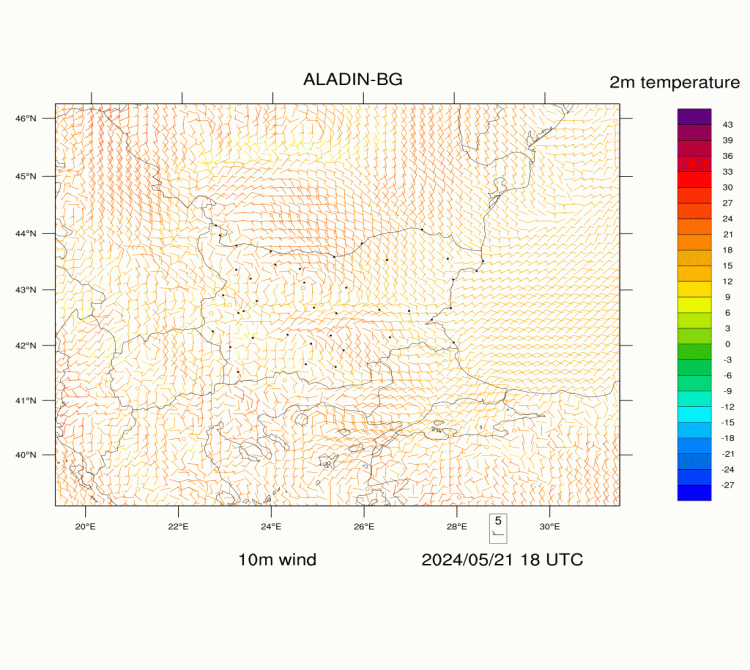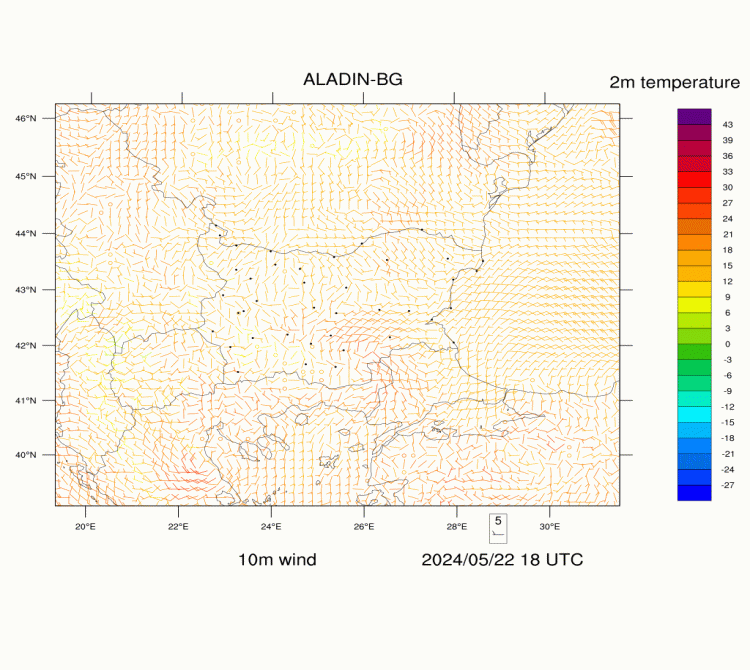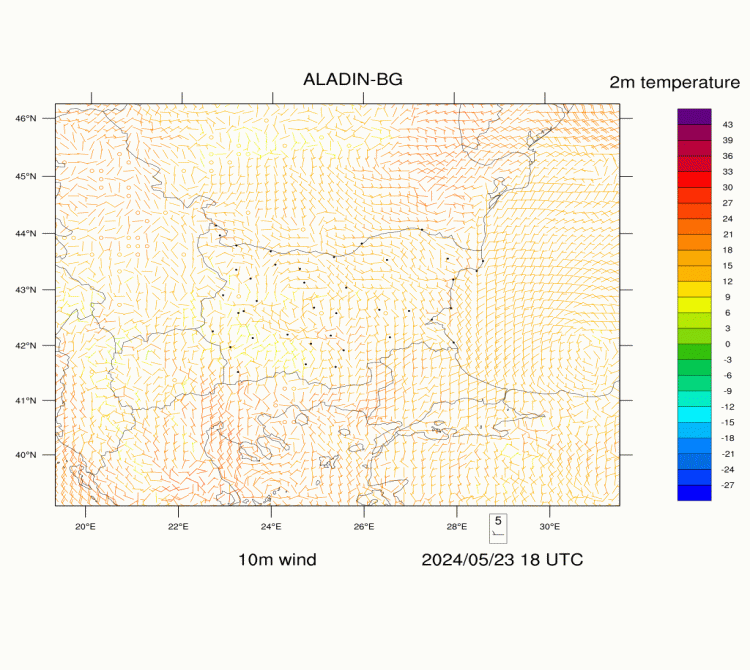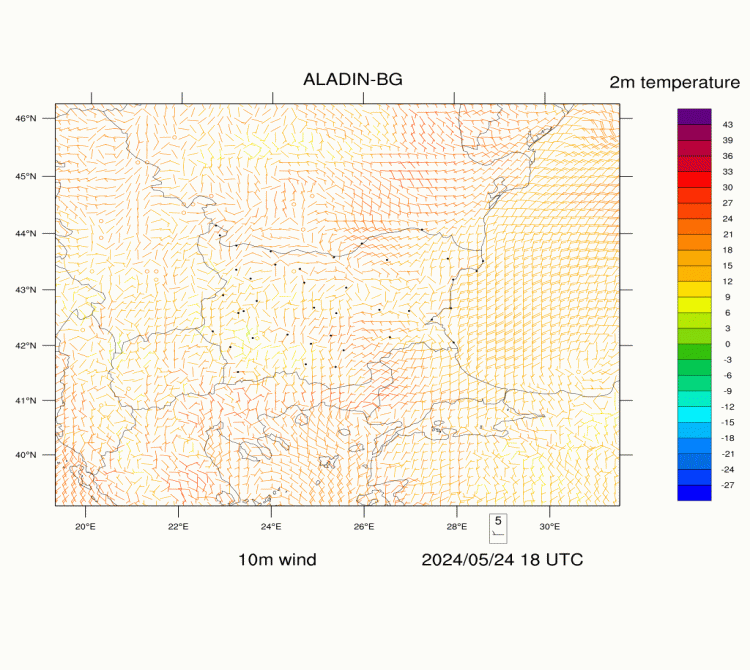
ALADIN-BG—Surface Wind and Temperature
AROME-BG—Temperature
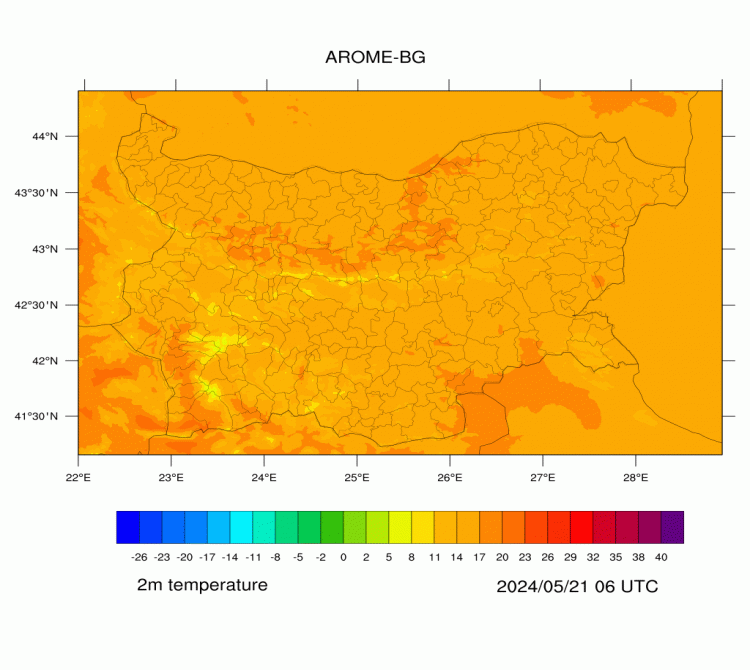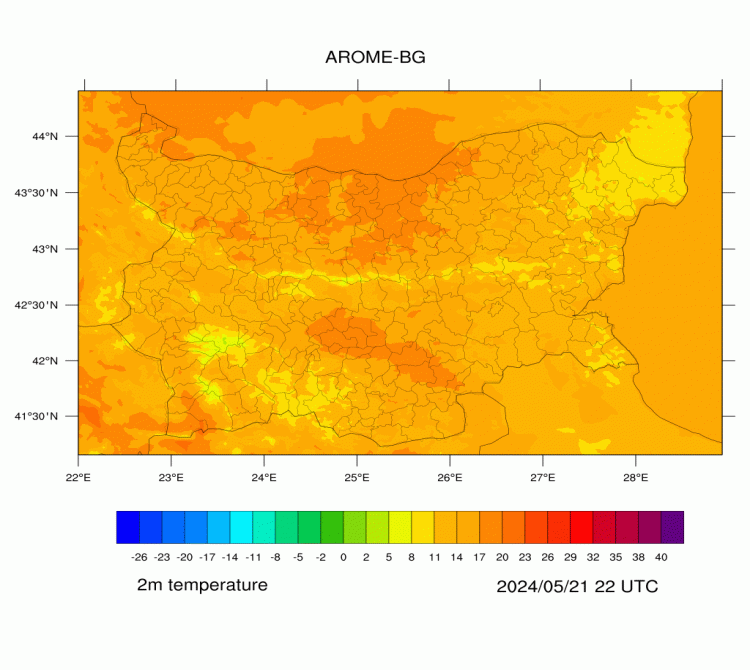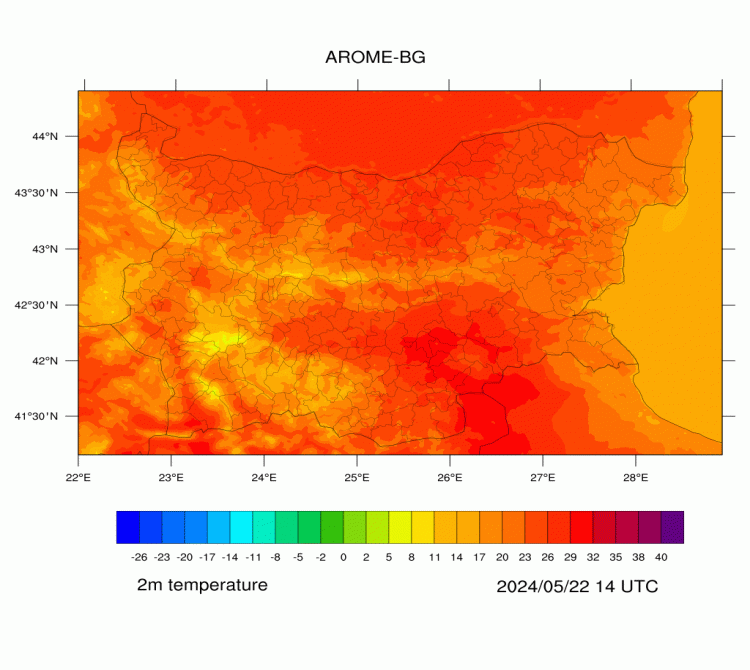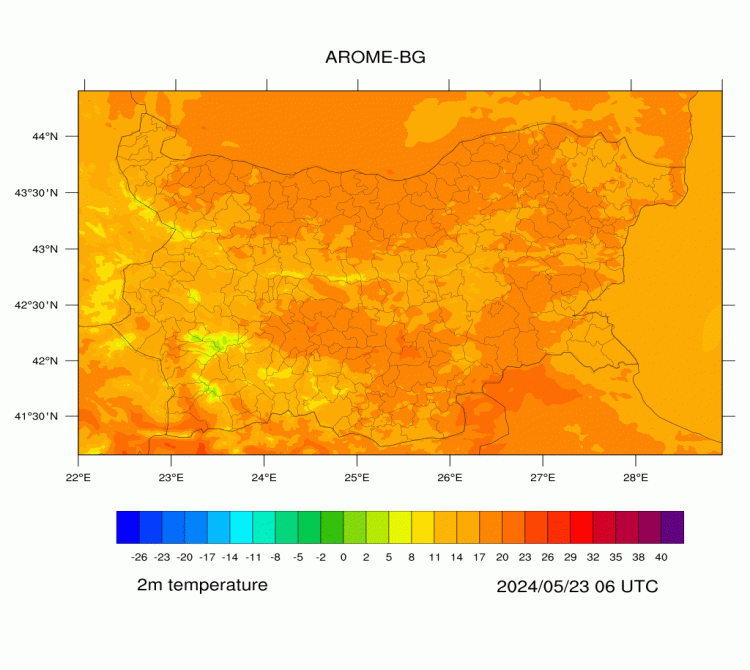
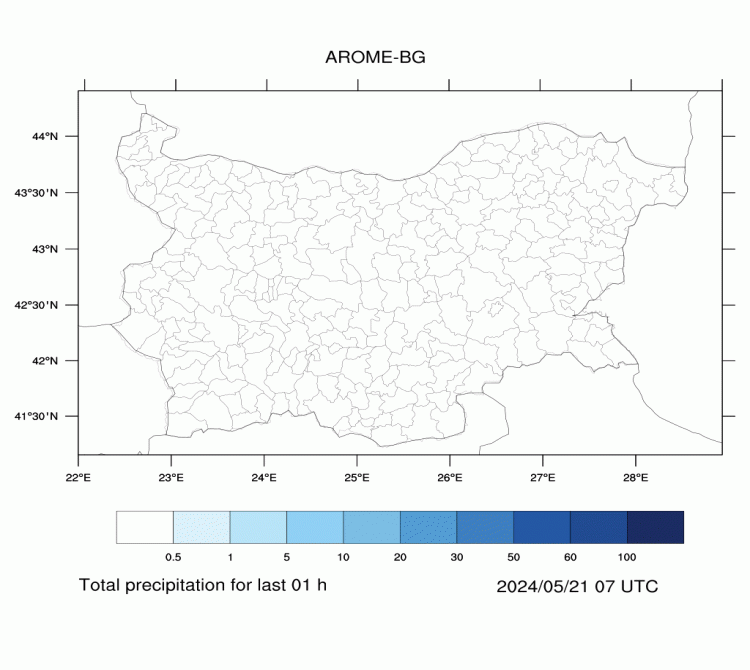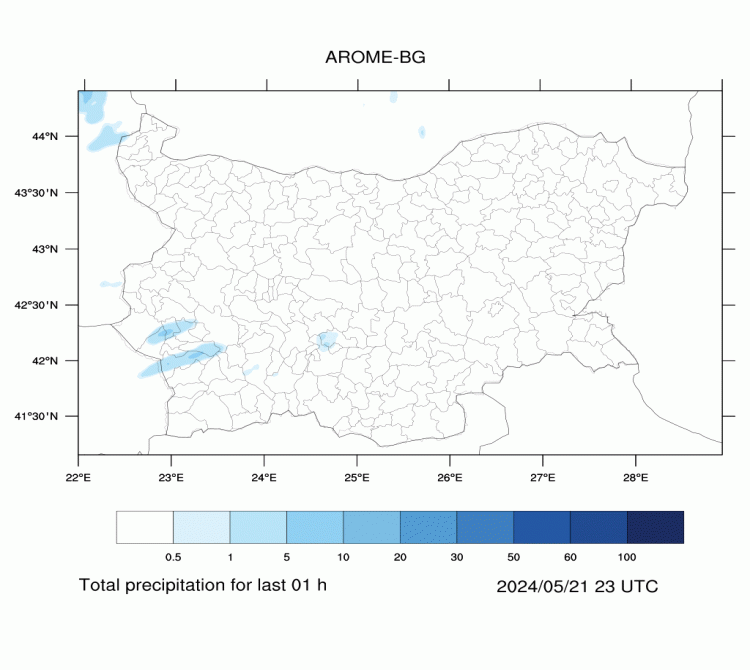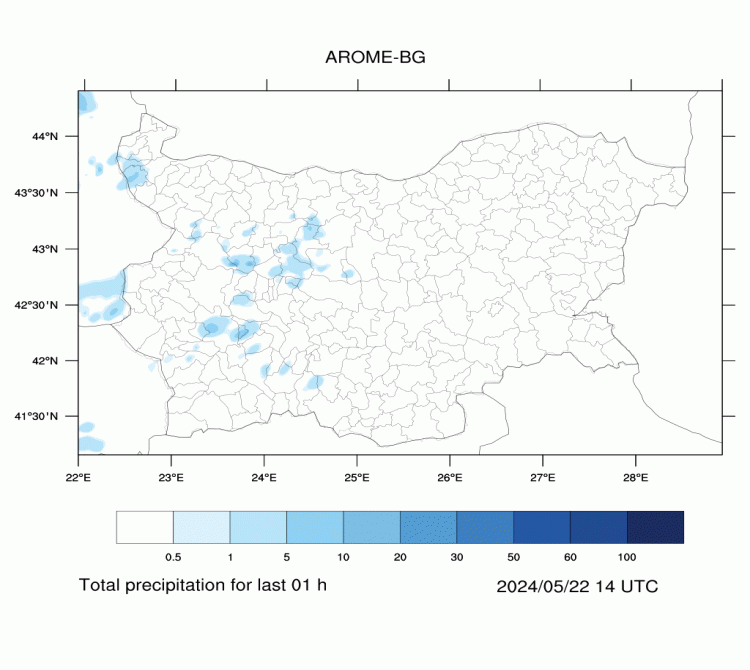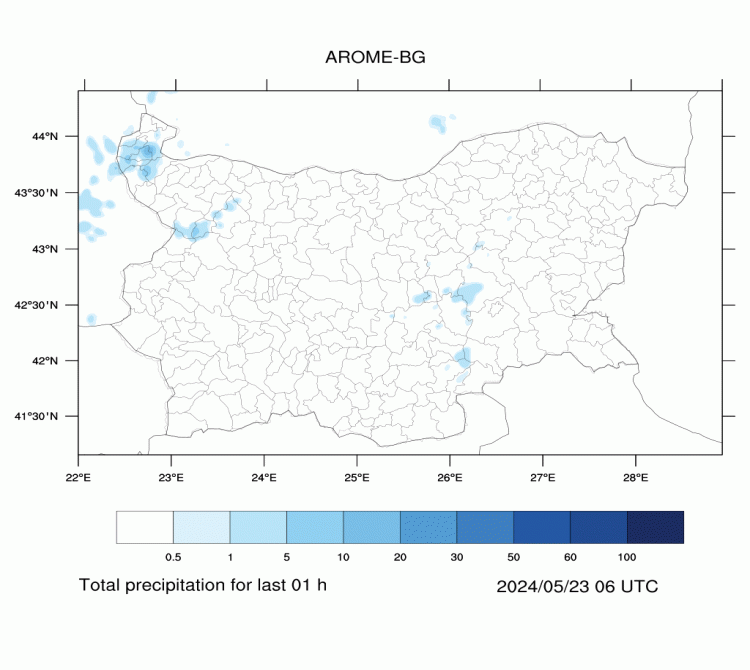
AROME-BG—Precipitation
Operational Frost Probability Forecasting System
Comfort Index
The maps are generated on the basis of the forecast of ALADIN-BG weather model.
The proposed maps show the current or expected feeling of thermal comfort/discomfort of the majority of people. The maps refer to a standard time of day, which corresponds to the classical observation periods at weather stations. For example, 12 UTC (Coordinated Universal Time) corresponds to 14:00 Bulgarian time (15:00 summer time), which is usually close to the warmest hours of the day, and 03 UTC corresponds to 05:00 Bulgarian time (06:00 summer weather) which is usually close to the coldest hours of the day.
Thermal Comfort Classes, Description of the Sensation of Comfort/Discomfort and Recommended Clothing
The table shows the degrees of thermal comfort/discomfort. The categories of comfortable, warm and hot are defined on the basis of the degrees of physiological stress to which the human thermoregulatory system is subjected in the different temperature conditions according to the feels like temperature. The categories for cold are according to the Wind Chill Index.
| Thermal comfort class | From feels like temperature, °С | To feels like temperature, °С | Grade in colour | Thermal sensation of comfort or discomfort | Description | Level of clothing |
| 13 | 44 | - | Extreme heat | Substantial risk of thermal shock in prolonged work/stay outdoors. | 0.4 | |
| 12 | 38 | 44 | Very hot | The mechanism of self-cooling by sweating is hindered. | 0.4 | |
| 11 | 32 | 38 | Hot | Almost the whole body is covered in sweat. | 0.4 | |
| 10 | 26 | 32 | Very warm | A big part of the body is covered with sweat. | 0.4 | |
| 9 | 20 | 26 | Warm | Sweating has started. A small part of the body is covered with sweat. | 0.5-0.4 | |
| 8 | 10 | 20 | Comfortable | Sensation of thermal comfort with suitable clothing | 1.0-0.5 | |
| 7 | 0 | 10 | Cool | Thermal comfort can be achieved with suitable clothing, but there is slight discomfort in the cold side on exposed parts of the body. | 1.5-1.0 | |
| 6 | -10 | 0 | Cold | Goosebumps start. | 2.0-1.5 | |
| 5 | -18 | -10 | Very cold | Shivering starts. | 2.4-2.0 | |
| 4 | -27 | -18 | Possible frost bite | Possible frost bite of bare skin | 2.9-2.4 | |
| 3 | -35 | -27 | Frost bite of bare skin | Frost bite of bare skin within 30 min of exposure | 3.3-2.9 | |
| 2 | -47 | -35 | Rapid frost bite of bare skin | Frost bite of bare skin within 10 min of exposure | 3.9-3.3 | |
| 1 | - | -47 | Dangerously rapid frost bite | Dangerously rapid frost bite with 5 min of exposure | 4.0 |
Clothing Index—Meaning
| Recommended clothing ensemble | Clothing index |
|---|---|
| Nude | 0 |
| Shorts | 0.1 |
| Shorts, open-neck shirt with short sleeves, sandals | 0.35 |
| Long light-weight trousers, open-neck shirt with short sleeves, open shoes | 0.5 |
| Long trousers, open-neck cotton work shirt with long sleeves, shoes | 0.7 |
| Long trousers, cotton work shirt with long sleeves, shoes, and a light jacket | 0.9 |
| Typical business suit (long trousers, cotton work shirt with long sleeves, vest, shoes, and a jacket) | 1.0 |
| Typical business suit and a cotton coat | 1.5 |
| Long resistant trousers, woolen flannel shirt, woolen socks, shoes, wind and water resistant jacket and vest, a hat and gloves | 1.5-2.0 |
| Polar weather suit with hood, warmth-keeping shoes, a hat covering the ears, strong isolating gloves | 3.0-4.0 |
Felt Temperature
Felt temperature is air temperature in a reference atmospheric environment where a person's sense of thermal comfort/discomfort would be the same as in real weather conditions. The feeling of thermal comfort is calculated using a full numerical model of thermal balance of the body of a "standard" human placed in atmospheric conditions near ground, outdoors, on grass or snow cover, if available. The feeling of thermal comfort/discomfort depends on the morphological parameters of the person - age, sex, height, weight and others, but for general purposes, the parameters of a "standard" person are used here. This is a 35-year-old man, 1.75 m tall, weighing 75 kg, in good health. The felt temperature depends on the work performed by the person and can be calculated at different power. In this case, it is assumed that the "standard" person performs work with applying the power corresponding to walking at a speed of 4 km/h on a horizontal surface. It is assumed that the wind always blows to the side of the direction of walking. The clothing is adapted (summer/winter) so that the "standard" person, if possible, achieves thermal comfort in the specific outdoor weather conditions. To determine the felt temperature, data on meteorological elements in the layer of air near the earth's surface (0–2 m), where the "standard" person is located, are used: air temperature; relative air humidity; wind speed; presence of snow cover. Also used: amount of cloud cover; geographical coordinates and altitude of the place; date and time.