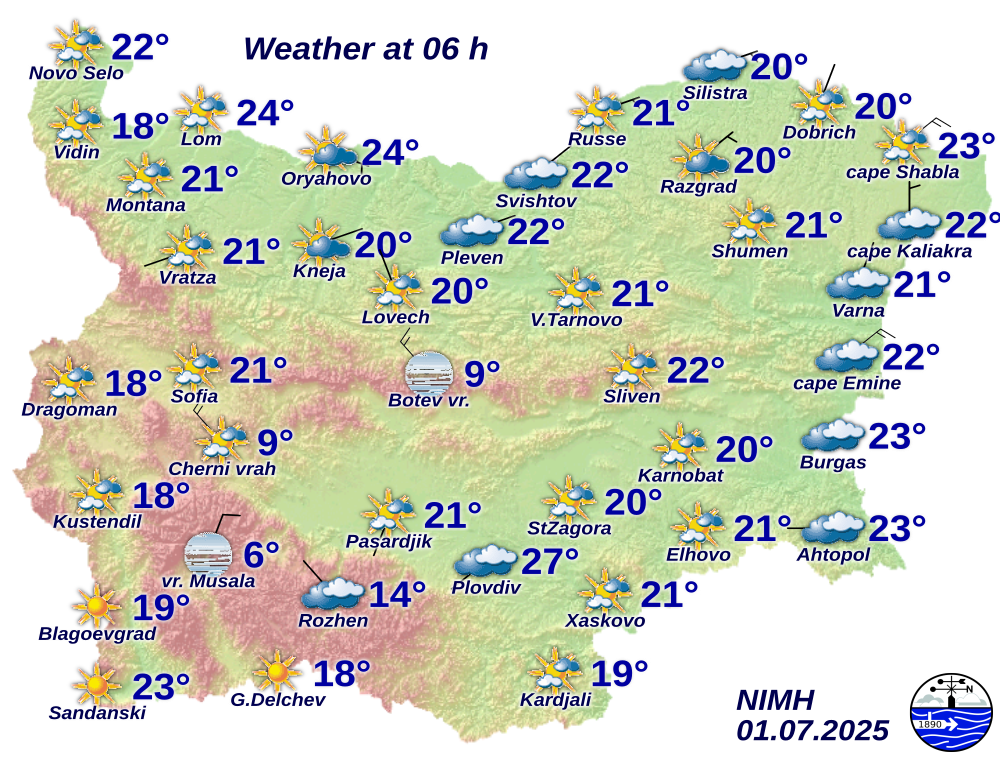
WEATHER FORECASTS
National Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology
Latest Measurements
| Station | Date | Hour | Temperature [°C] | Weather | Wind speed [m/s] | Wind direction | Air pressure [hPa] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Novo Selo | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 8 |  recent fog recent fog | 0 | тихо | 1016.2 |
| Vidin | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 8 |  partly cloudy partly cloudy | 2 | E | 1019.6 |
| Vratsa | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 4 |  fog fog | 2 | NW | 985.4 |
| Montana | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 5 |  fog fog | 1 | E | 998.2 |
| Lom | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 6 | 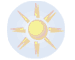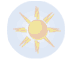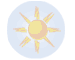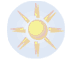 mist mist | 1 | N | 1020.9 |
| Oryahovo | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 3 |  fog fog | 0 | тихо | 1020.7 |
| Knezha | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 4 |  recent fog recent fog | 2 | W | 1008.7 |
| Lovech | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 10 |  partly cloudy partly cloudy | 1 | NE | 995.4 |
| Pleven | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 4 |  fog fog | 2 | N | 1003.5 |
| V. Tarnovo | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 11 |  clear/sunny clear/sunny | 0 | тихо | 998.4 |
| Svishtov | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 9 |  clear/sunny clear/sunny | 1 | NE | 1018.2 |
| Ruse | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 11 |  partly cloudy partly cloudy | 3 | N | 1018.2 |
| Shumen | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 10 |  clear/sunny clear/sunny | 2 | E | 995.7 |
| Razgrad | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 10 |  clear/sunny clear/sunny | 2 | NE | 980.7 |
| Silistra | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 8 |  clear/sunny clear/sunny | 0 | тихо | 1020.4 |
| Silistra-NIMH | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 9 |  clear/sunny clear/sunny | 2 | W | 1022.2 |
| Varna | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 12 |  clear/sunny clear/sunny | 2 | SE | 1017.8 |
| Shabla | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 9 |  clear/sunny clear/sunny | 4 | N | 1022 |
| Kaliakra | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 11 |  clear/sunny clear/sunny | 2 | NW | 1014.9 |
| Dobrich | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 11 |  clear/sunny clear/sunny | 2 | N | 997.4 |
| Murgash | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 0 |  partly cloudy partly cloudy | 2 | E | 832.5 |
| Kyustendil | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 10 |  clear/sunny clear/sunny | 0 | тихо | 958 |
| Dragoman | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 11 |  clear/sunny clear/sunny | 3 | SE | 937.2 |
| Blagoevgrad | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 9 |  clear/sunny clear/sunny | 1 | W | 970.6 |
| Cherni Vrah | 13.03.2026 | 11 | -3 |  partly cloudy partly cloudy | 10 | E | 772.1 |
| Sofia | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 7 |  clear/sunny clear/sunny | 1 | N | 951 |
| Mussala | 13.03.2026 | 11 | -7 |  partly cloudy partly cloudy | 6 | E | 711.3 |
| Plovdiv | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 8 |  mist mist | 0 | тихо | 1003.9 |
| Botev | 13.03.2026 | 11 | -4 |  partly cloudy partly cloudy | 6 | E | 762.1 |
| Pazardzhik | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 7 |  cloudy cloudy | 2 | N | 997.9 |
| Chirpan | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 9 |  partly cloudy partly cloudy | 4 | W | 1001.2 |
| Kazanlak | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 9 |  partly cloudy partly cloudy | 3 | S | 973 |
| Stara Zagora | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 11 |  clear/sunny clear/sunny | 1 | SE | 1002.1 |
| Sliven | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 11 |  clear/sunny clear/sunny | 3 | S | 991.6 |
| Elhovo | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 10 |  clear/sunny clear/sunny | 2 | N | 1001.4 |
| Karnobat | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 11 |  clear/sunny clear/sunny | 2 | E | 999.4 |
| Emine | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 9 |  clear/sunny clear/sunny | 6 | N | 1015.2 |
| Burgas | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 9 |  clear/sunny clear/sunny | 3 | SW | 1019.4 |
| Ahtopol | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 8 |  cloudy cloudy | 4 | N | 1021 |
| Sandanski | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 12 |  clear/sunny clear/sunny | 1 | W | 995.2 |
| Gotse Delchev | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 10 |  clear/sunny clear/sunny | 2 | SE | 949.9 |
| Rozhen | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 3 |  mostly cloudy mostly cloudy | 2 | NE | 825.8 |
| Kurdzhali | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 10 |  cloudy cloudy | 4 | N | 983 |
| Haskovo | 13.03.2026 | 11 | 10 |  partly cloudy partly cloudy | 4 | N | 994 |
Legend—Measurements
| Symbol | Weather | Symbol | Weather | Symbol | Weather | Wind—Symbol | m/s | km/h | Knots |
 | clear/sunny |  | recent drizzle |  | heavy drizzle |  |
0 | 0 | 0 |
 | partly cloudy |  | drizzle and rain; recent rain; slight rain shower(s); |  | moderate rain; | 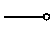 |
2 | 7 | 3 |
 | mostly cloudy |  | recent snow; light snow; snow or crystals |  | moderate rain; moderate rain shower(s); | 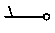 |
3,5 | 12 | 7 |
 | visibility reduced by smoke,dust or sand;dust or sand whirl(s);mist; |  | rain and snow |  | heavy rain | 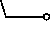 |
5 | 18 | 12 |
 | duststorm or sandstorm; thick fog; |  | freezing drizzle/rain |  | violent rain shower(s) | 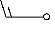 |
8 | 28 | 17 |
 | haze; shallow fog; |  | recent snow shower;light snow; |  | rain and snow |  |
10 | 36 | 22 |
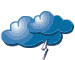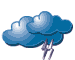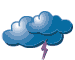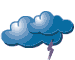 | lightening(s) |  | recent hail; sleet; hail; |  | heavy snow; snow shower(s) | 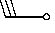 |
15 | 55 | 32 |
 | rain shower, not falling; cloudy |  | blowing snow; moderate snow; snow shower(s); |  | diamond dust,sleet | 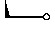 |
25 | 90 | 52 |
 | shower near the station |  | light or dissipating fog; |  | heavy rain and snow | 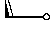 |
30 | 110 | 62 |
 | squall(s); tornado; recent thunder; |  | light or moderate drizzle; |  | hailstorm | 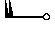 |
50 | 180 | 102 |
Minimum and Maximum Temperatures
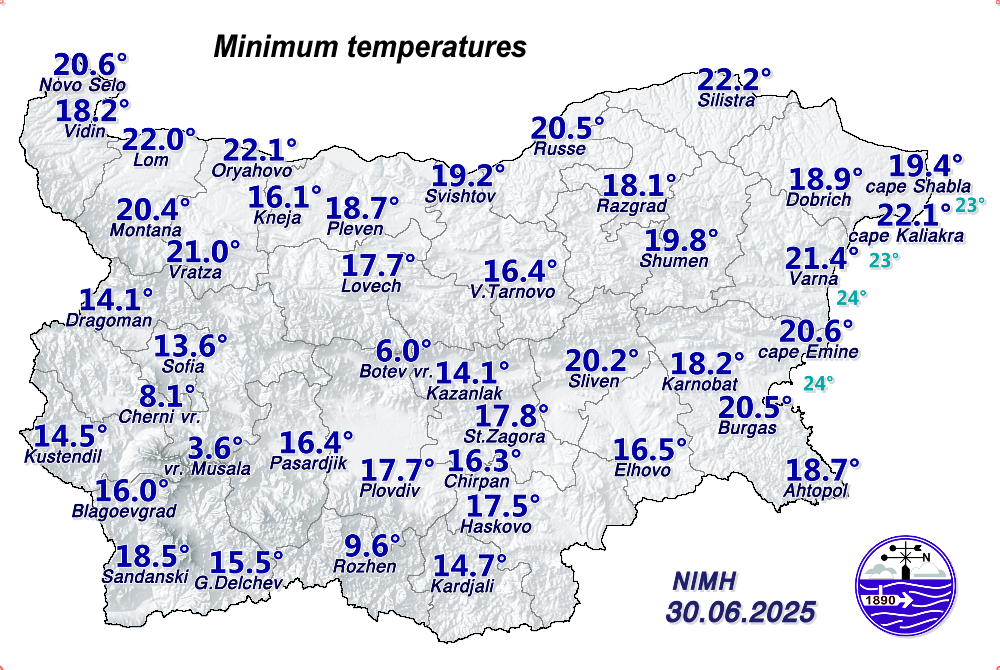
What do you see on the maps with the minimum and maximum temperatures? On the map with the minimum/maximum measured temperatures by synoptic station, you will see one value in degrees Celsius (℃) above the written name of each city that has a NIMH synoptic station. It is the minimum/maximum value recorded by the measurements in the corresponding way for that particular day. At the bottom right of the map is the date to which the corresponding temperature measurements relate.
Air temperature: air temperature is a measure of the average thermal energy of ambient air molecules—the higher the temperature, the higher the kinetic energy of the molecules. Historically, the most common instrument used was a glass thermometer with liquid that expands or contracts as a result of heating or cooling. Mercury was the most commonly used. Mercury thermometers are not used in meteorology for almost a decade, as mercury is dangerous if it leaks when the thermometer breaks. In meteorological services around the world, including the National Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology (NIMH), as part of the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), these thermometers have been replaced by those with alcohol-based liquid or digital thermometers. Modern automatic weather stations use an electronic sensor. The measurement accuracy of these sensors depends on the material from which they are made. High accuracy is achieved, for example, with sensors made of platinum. In order to measure the temperature most accurately, the instruments are placed under radiation protection - a meteorological cell of special construction so as to avoid the influence of direct heating from the Sun. The construction of the meteorological cell allows air to pass through it unhindered, it always faces north and is painted white. Combined with the compulsory positioning of the instrument cage 2 metres above the ground on a grassed mown area, avoids a maximum number of disturbances in the measurements and guarantees the reading of the actual air temperature. In NIMH, according to the standard WMO recommendations, the daily maximum (highest) and minimum (lowest) temperature are recorded once a day, at 06 UTC (08:00/09:00 - in winter/summer time in Bulgaria) and at 18 UTC (20:00/21:00 - in winter/summer time in Bulgaria), respectively, while instantaneous air temperature measurements can be made at any time of the day, practically continuously.
How is temperature measured for meteorological purposes? Temperature data before 1910 should be used with extreme caution, as many stations before that date were set up in substandard locations, some of which gave readings that were several degrees higher or lower than those measured according to post-1910 standards. Daily maximum temperatures are usually observed in the afternoon, and daily minimum temperatures at night or around dawn. In clear and calm weather, the temperature minimum is reached around sunrise. That is, the usual diurnal pattern is associated with a minimum in the morning and a maximum after noon. There are also exceptions, which are associated with certain synoptic conditions with cold intrusion, the temperatures have a so-called "reverse diurnal course", which means that it is colder in the afternoon than in the morning.
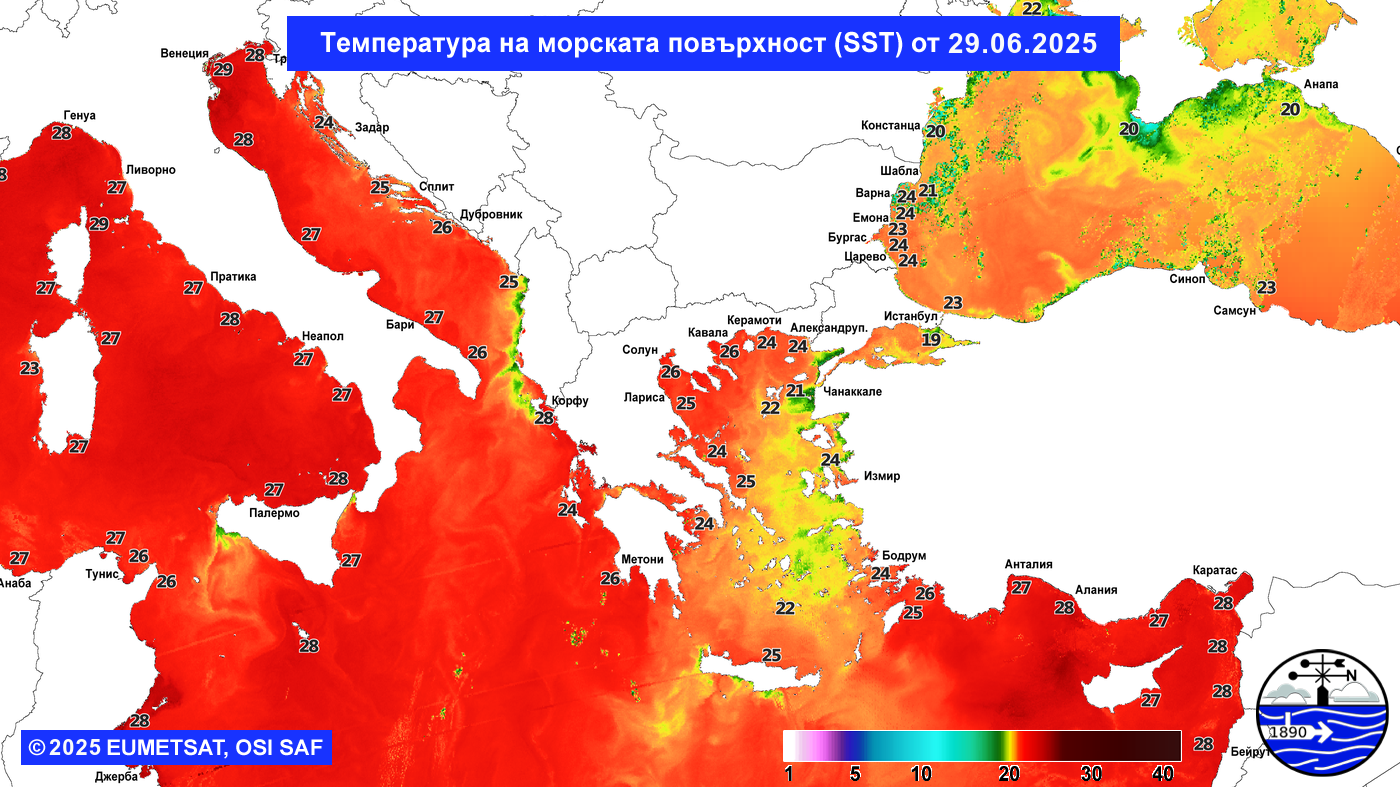
Satellite IR
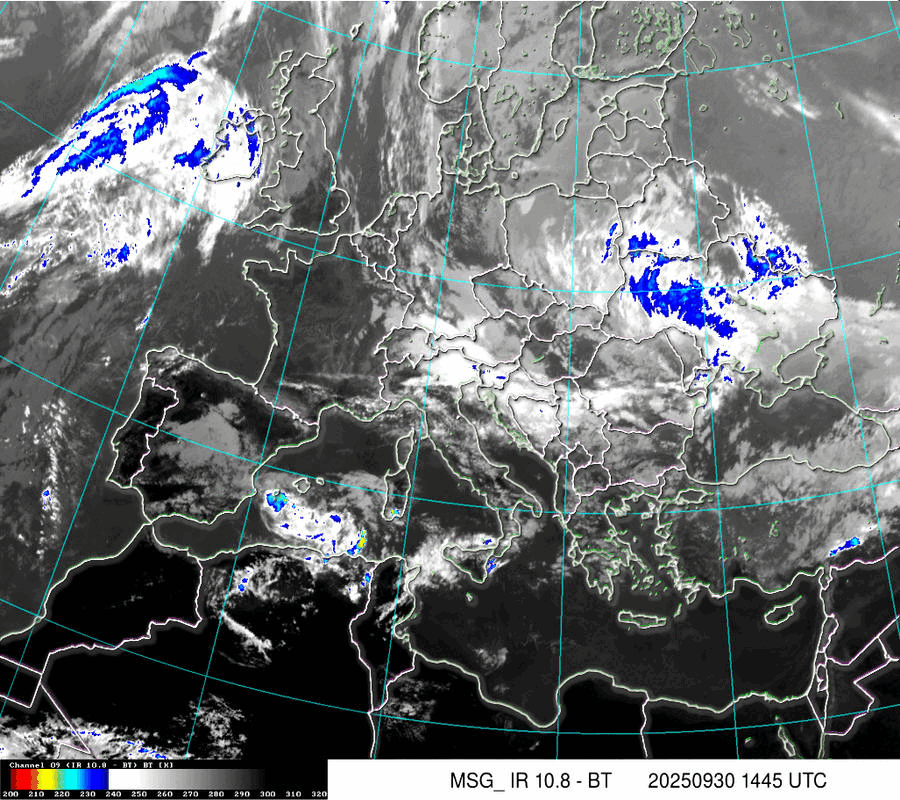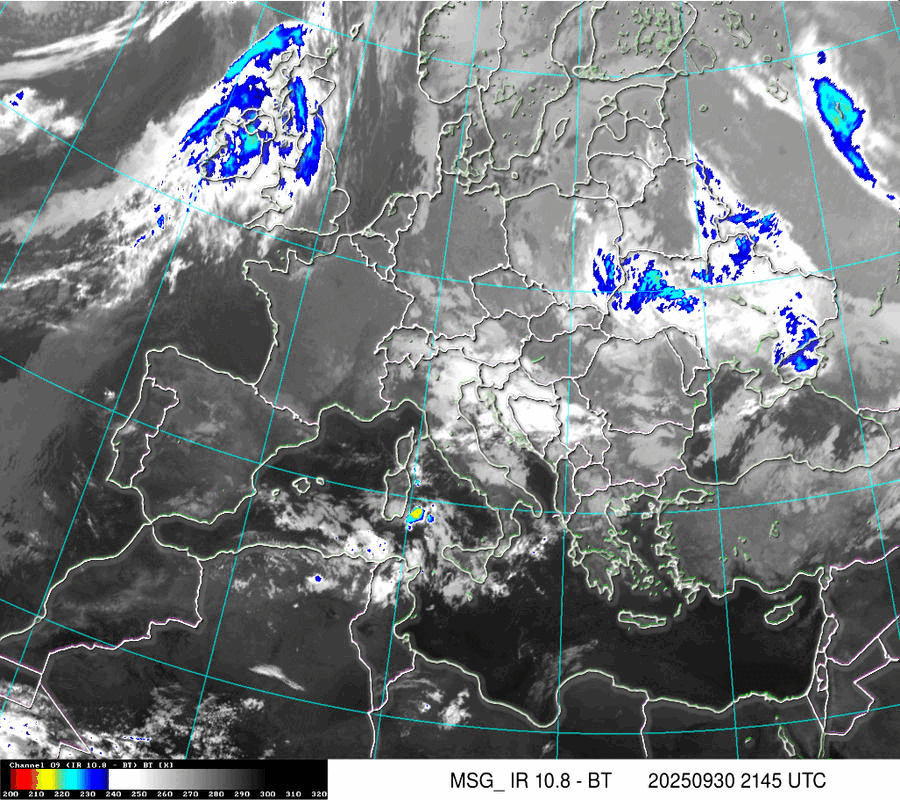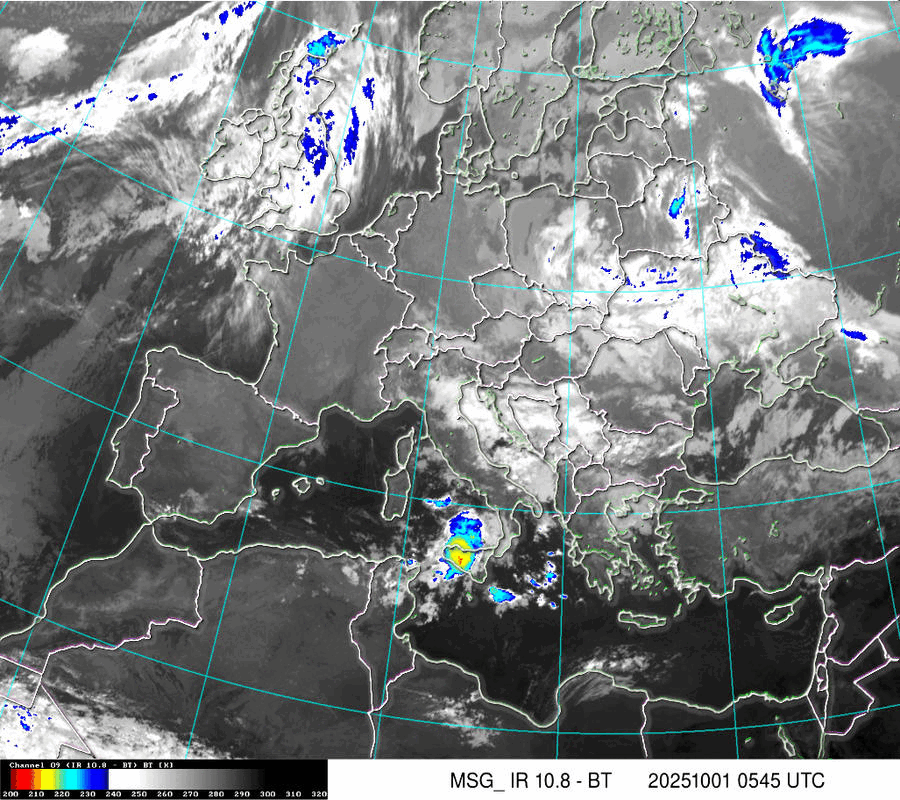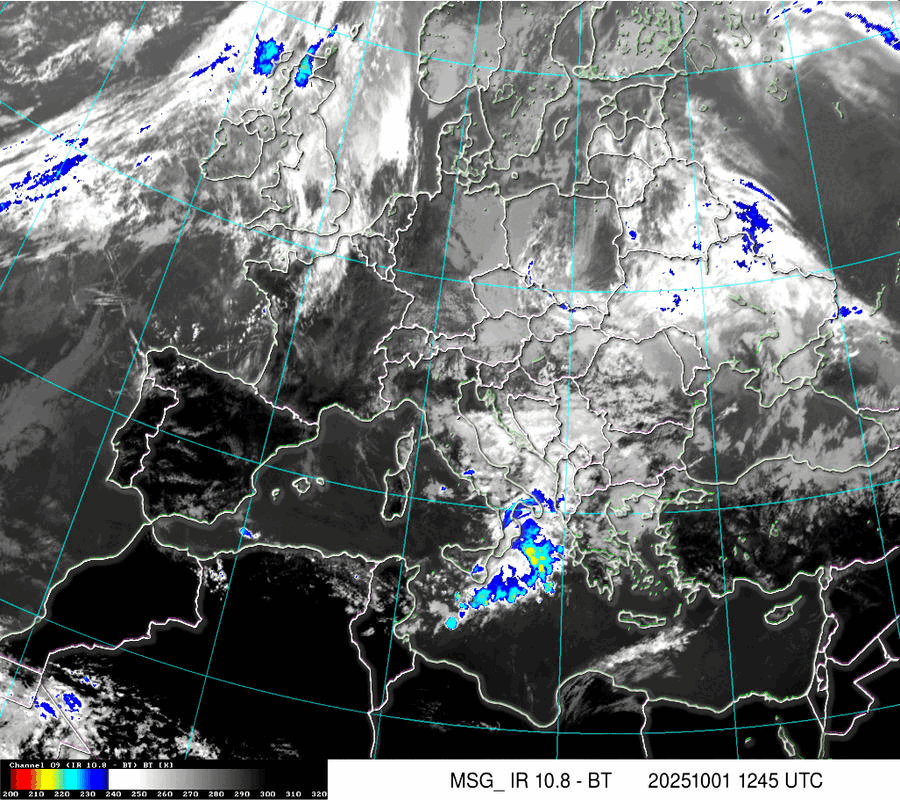
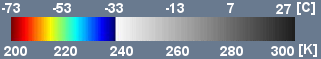
Cloud Systems
(Temperature of cloud tops or land/sea surface if clouds are missing)
The scale is in Kelvin, dublicated in °C.:
Satellite RGB
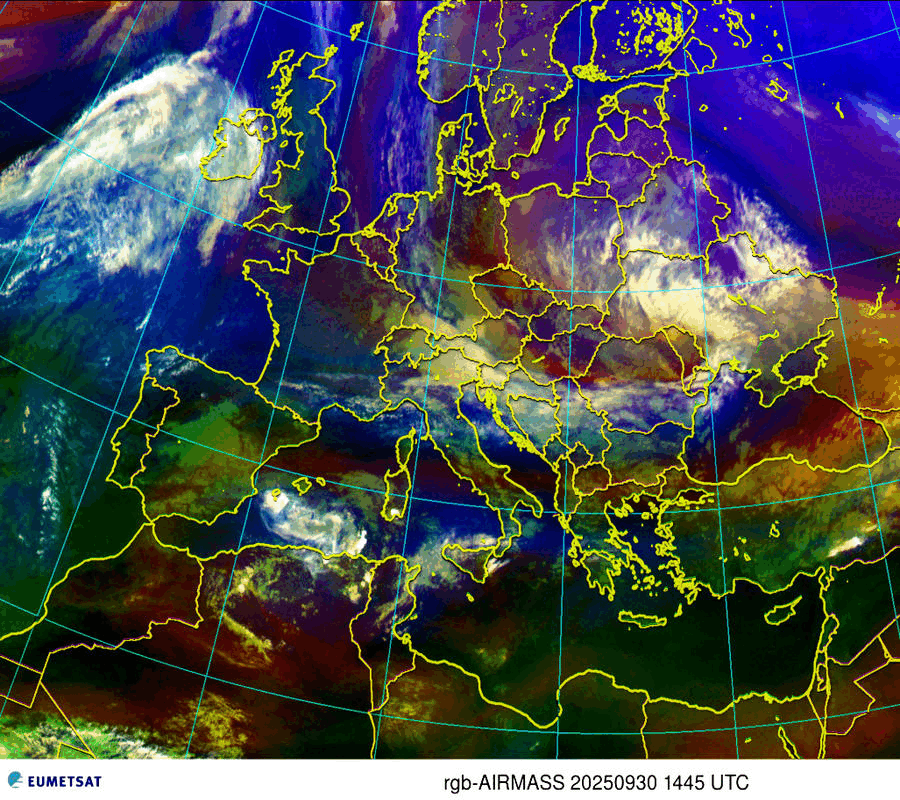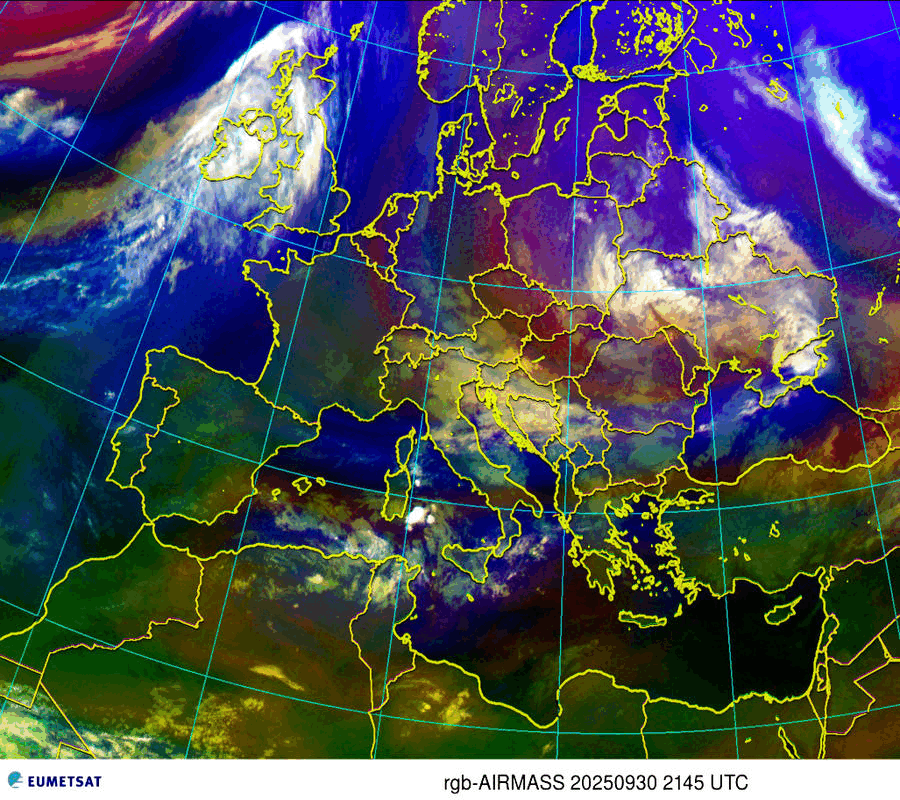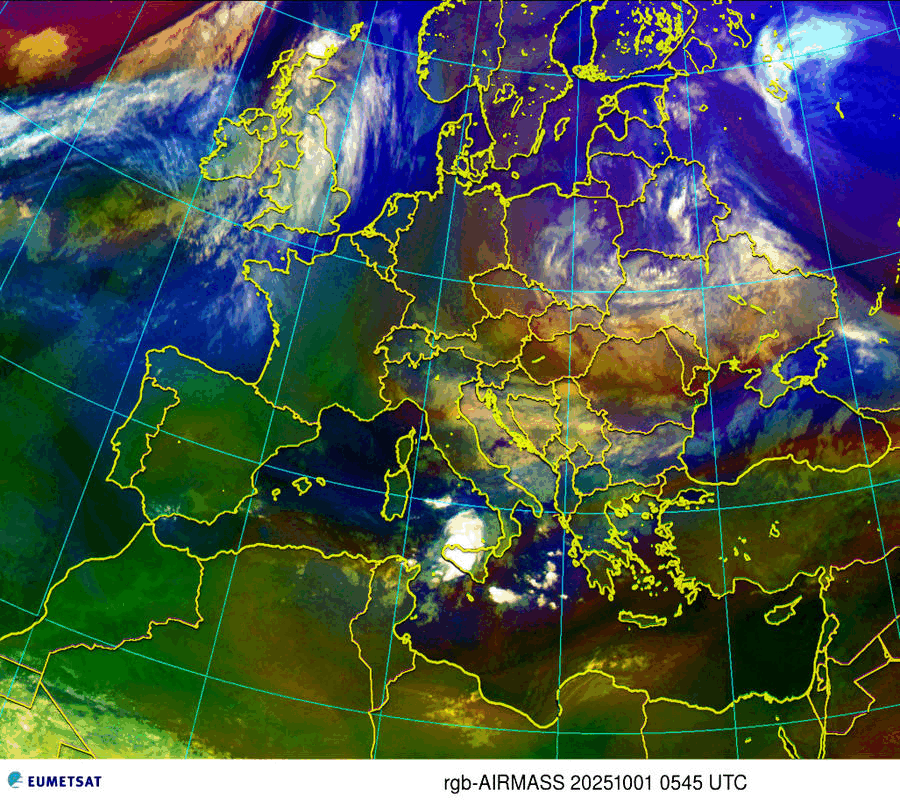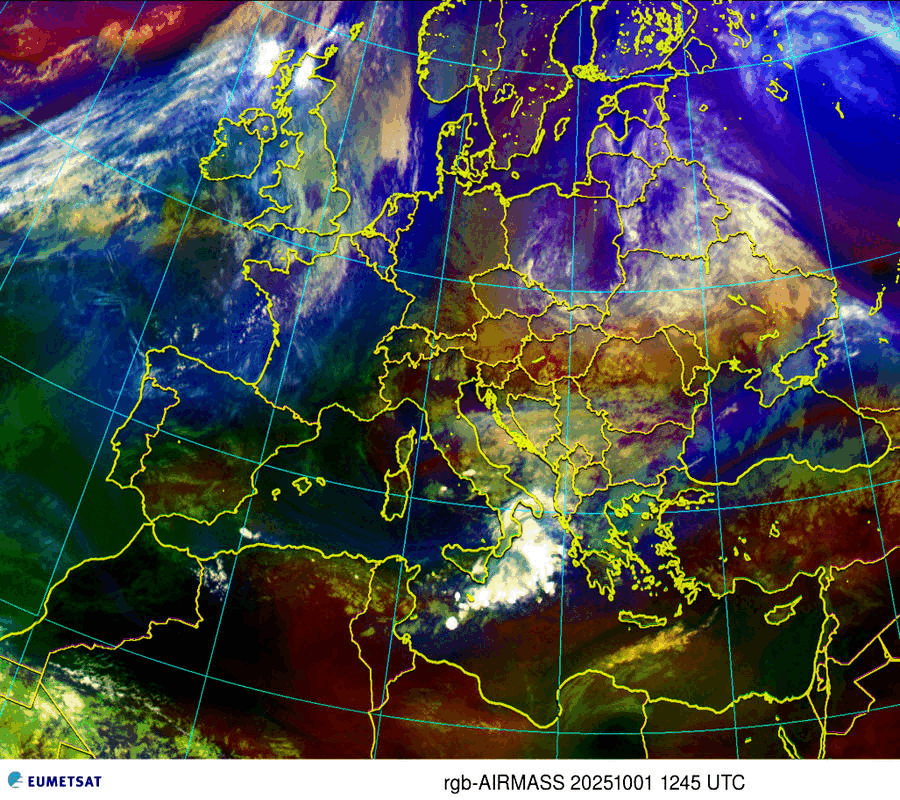
Airmasses
 | Thick high-level clouds |
 | Thick mid-level clouds |
 | Jet stream, high Potential Vorticity (PV) |
 | Cold airmass |
 | Warm airmass – high tropopause |
 | Warm airmass – low tropopause |
EUMETSAT is the European intergovernmental satellite organisation for monitoring weather, climate and the environment.
EUMETSAT operates and develops the European system of meteorological satellites monitoring the atmosphere and ocean and land surfaces which deliver weather and climate-related satellite data, images and products – 24 hours a day, 365 days a year. This information is supplied to the National Meteorological Services of the organisation's Member and Cooperating States (in Bulgaria—NIMH) as well as other users worldwide.
Bulgaria is a Cooperating State EUMETSAT since May 25, 2005.
24-hour Precipitation Map

24-hour precipitation sum analysis since 8 h local time on 27.06.2023 until 8 h on 28.06.2023, using ALADIN numerical model and measured data from NIMH stations. It is calculated once daily about 12 o'clock. It is produced automatically and may sometimes contain inaccurate data that is corrected later.

Snow Cover

Snow depth from NIMH stations at 7h 30min on the date, given on the map. Calculated once a day at about noon. Left scale — snow depth in centimeters. Right scale — altitude in meters for places without snow.
Notice: This is an operational map and is only suitable as a guide to the general state of snow cover in the country. It contains inherent imperfections as a result of modelling methods and operational data transmission.

Daily Data for the Snow Cover in 166 NIMH Stations
за 13.03.2026
|
LegendThe table gives data on the amount of precipitation in "lines" (tenths of a millimeter or tenths of a liter per square meter) in the left column, on the type of precipitation - in the middle column, and on the presence of snow cover and its height (in centimeters) – in the right column. When there is no number in the left data column, there is no precipitation. Climate stations report precipitation data every day. In case there is no information for a given date, n.a. is written in the middle column. Since 2021, the network of rain gauge stations at NIMH has been equipped with automated devices for real-time rainfall measurement, but the rain gauge stations continue to provide operational information of the 24-hour rainfall amount in the classic way once a day. Traditionally, it is only reported for days with measured precipitation ≥ 0.5 mm, but it is possible to have days with information for precipitation < 0.5 mm, and this is not wrong. For these stations, it is possible that there are days when there is precipitation, but no information is reported. For this type of station, an empty field means that no information has been received for the corresponding date. Also for this type of station information n.a. in all three columns means that wrong information has been received for that date and has been corrected.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Note 1: Data are operational. Errors are possible. To be used for decision making only after consultation with the weather forecaster on duty. Note 2: At Moussala - a mountain station - snow cover is not measured. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lightening Detection over Bulgaria
UTC - Summer daylight saving time in Bulgaria is UTC+3, in Winter the local time is UTC+2
Hourly (in UTC) and space distribution of lightenings registerred over Bulgaria during the last day - from 0h to 24h
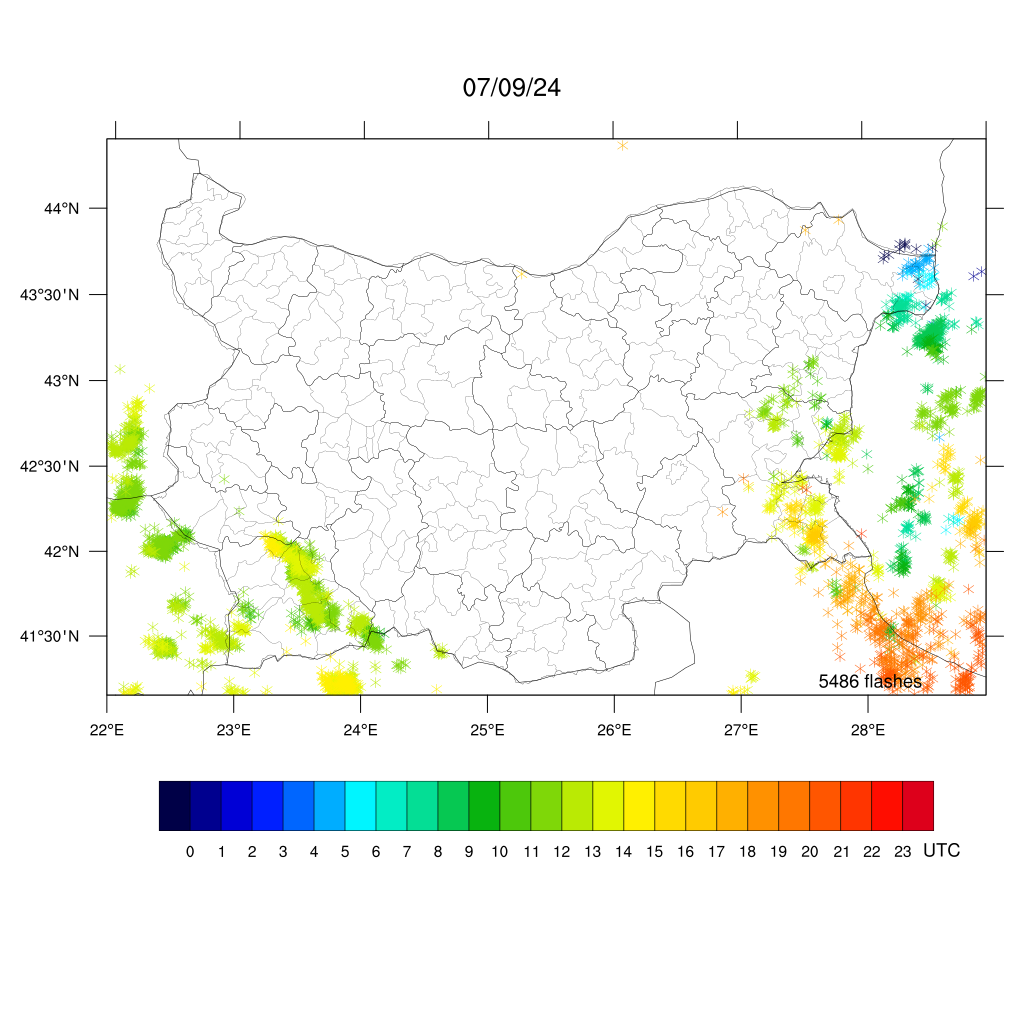
Hourly (in UTC) and space distribution of lightenings registerred over Bulgaria today (updated hourly)

The system LEELA (Lightning Electromagnetic Emission Location by Arrival time difference) LEELA (Lightning Electromagnetic Emission Location by Arrival time difference) of the British Met Office is the new automatic lightning detection network. It consists of ten sensors deployed across Europe to determine the location and timing of recorded lightnings.